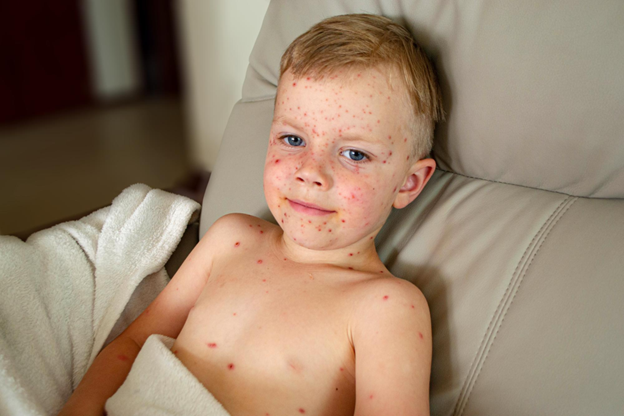
Chicken pox, a common yet highly contagious illness, can be tricky to spot early on. Identifying the symptoms promptly is crucial to prevent its spread. Chicken pox symptoms can vary from mild to severe, making early detection significant. Knowing what to look for helps keep others safe and start recovery sooner. With chicken pox being so contagious, acting fast is essential.
Understanding Chickenpox: A Brief Overview
Chickenpox is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Typically, it’s more common in children but can affect anyone who hasn’t been vaccinated or previously infected. The virus spreads easily through coughs, sneezes, or sharing of belongings. The chicken pox contagious period usually starts one to two days before the rash appears, and it continues until all the blisters have crusted over. This period can make containment difficult as a person might unknowingly spread the virus even before they show any noticeable symptoms.
Detecting Early Warning Signs of Chickenpox
Before the classic rash appears, some subtle chicken pox symptoms can tip you off. About one to two days before the rash, watch for a mild fever, fatigue, and general discomfort. Children may also show signs like irritability, loss of appetite, headache, and mild body aches. Recognizing these early signs can lead to quick medical advice, which is key to managing the illness well. Early treatment can help reduce discomfort and prevent the disease from spreading to others.
The Classic Chickenpox Rash
The most distinct symptom of chicken pox is its rash. It often starts on the face, chest, and back before spreading elsewhere. The rash feels itchy and uncomfortable. Initially, it appears as small red spots that can easily be mistaken for insect bites or slight skin irritation. As it progresses, chicken pox symptoms like itching become more intense, leading to further scratching and potential spreading of the illness.
Stages of the Chickenpox Rash
- Stage 1: Begins as small red spots.
- Stage 2: These evolve into fluid-filled blisters.
- Stage 3: Blisters then turn into scabs over time. Recognizing these stages helps in understanding the illness’s timeline. Managing chicken pox during these stages reduces the chances of spreading and experiencing further complications.
Recognizing Other Common Symptoms
Beyond the rash, other chicken pox symptoms include fever and a general feeling of unwellness. Some may also experience decreased appetite and occasionally a mild cough or runny nose. Effectively managing these symptoms with rest and gentle care prevents complications. It’s essential to keep an eye on these signs to ensure a smoother recovery.
Chickenpox Across Different Age Groups
Chicken pox symptoms can differ between children and adults. In children, the illness is often milder with fewer spots. However, adults might experience more severe symptoms, including a higher risk of complications. Vaccinated individuals may have breakthrough cases, which are generally milder but still require attention. Understanding these differences is important for both personal health and public safety, preventing broader outbreaks and maintaining community health standards.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Chickenpox
Watch for signs of complications such as difficulty breathing, unusual drowsiness, or persistent cough. These may need medical care. High-risk groups, such as pregnant women or those with weakened immune systems, should be extra cautious. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures safe management of chicken pox.
Distinguishing Chickenpox from Other Rashes
Chicken pox symptoms can resemble other rashes, like those from measles or allergies. Noticing the pattern, location, and characteristics of the rash helps in differentiating. Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective treatment and limiting the spread of illness. By being aware and observant, unlike other rashes, chicken pox has a very distinct itchy vesicular rash.
Role of Vaccination in Preventing Chickenpox
The chicken pox vaccine plays a critical role in public health. It’s effective in preventing severe outbreaks and chicken pox symptoms. It’s recommended for children and unvaccinated adults to maintain a high level of community immunity. Receiving the vaccine reduces the incidence of the illness significantly, helping protect vulnerable groups.
Home Care and Management Tips
Taking care at home involves: – Rest and plenty of fluids. – To relieve itchiness, use soothing lotions or cold compresses. – Avoid scratching to prevent infection. Preventing chicken pox spread means maintaining good hygiene and limiting contact. Families play a crucial role in ensuring safe and effective care, promoting a quicker and smoother recovery.
Conclusion: The Power of Awareness
Being informed about chicken pox symptoms and prevention strategies is empowering. Knowing what to watch for can protect both you and those around you. Stay proactive about health concerns and consult healthcare providers when needed. This awareness makes a big difference in keeping communities healthy and safe.